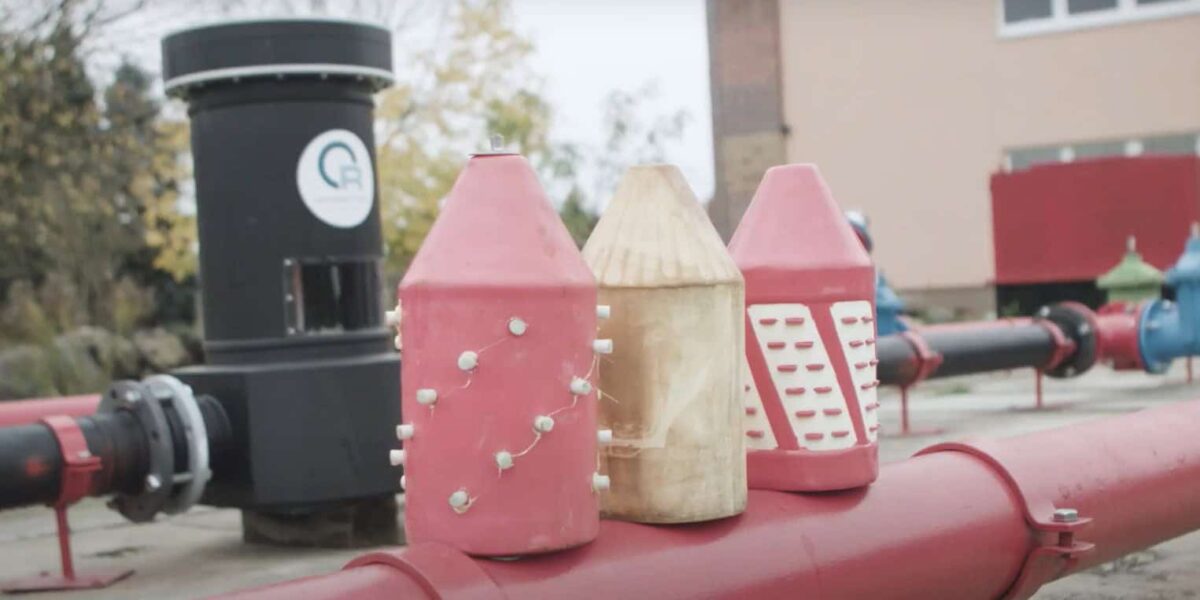

Pigs and how they are to use
A pipe pig is a versatile running or passing body for pipelines. With a slight difference between its outer diameter and the inner diameter of the pipe to be cleaned, the pig is ideal for ‘pushing out’ the contents hydraulically using its own drive or water and/or gas pressure. Pigs are also used for corrosion testing.
The cleaning pig – effective pipe cleaning
A cleaning pig is usually made of soft to hard plastic, such as PU (polyurethane), which can be equipped with metal nubs or brushes for heavy soiling. They are available in different versions to suit the individual conditions in the pipe. The usual shapes are cylindrical with a tip, spherical or tapered. In addition, disc pigs with a steel core mounted on plastic plates are also used for pipe cleaning.
Pipe cleaning pigs are used to thoroughly clean pipes. They remove deposits from the pipe walls. These include slime, grease, biofilm and iron and manganese deposits. Contaminants that have accumulated at the bottom of the pipe, such as sand or sediment, can also be removed.
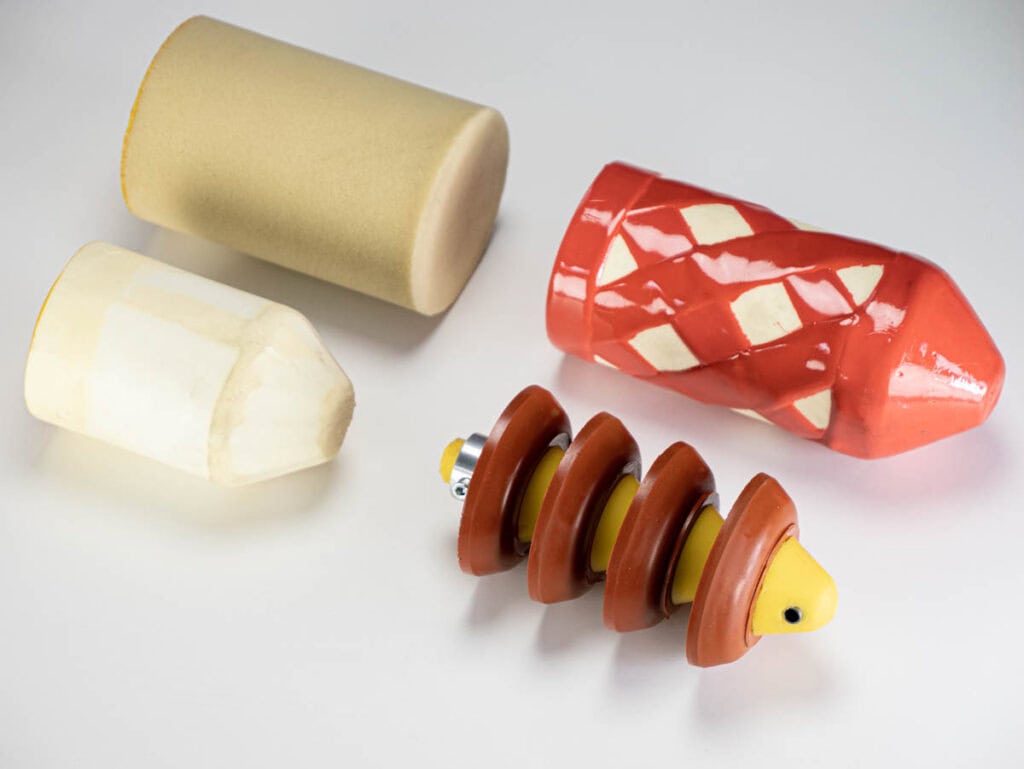


For this reason, regular use of pigging technology ensures that the pipeline functions properly, increases efficiency and reduces (pumping) costs.
The intelligent pig – effective pipe inspection
Intelligent pigs are used especially for larger pipe diameters, particularly in the oil and gas sector. These pigs usually feature a combination of round sealing plates at both ends and a tapered middle section. These pipe pigs are equipped with cameras and ultrasound devices to carry out inspection runs through the pipes. This allows potential faults or cracks to be detected and repaired at an early stage, thereby preventing more serious damage.
The companies Rosen and 3P Services from our neighbouring towns of Lingen and Wietmarschen in Germany offer inspections using these pigs.
Rosen
3P Services


Pipeline pigging: Why it pays off
Regular cleaning of pipelines prevents unwanted blockages and deposits. Pigging systems increase the service life of pipes and product yield while reducing flushing costs. They can be used in almost all areas of industry and can sometimes be applied during the process.
Pigging for clean pipes
Thanks to the use of cleaning pigs, dirt in the pipes is effectively loosened and pushed out. In contrast, not using pigs can lead to blockages in the pipes, which means that the medium can no longer flow through as usual. Deposits in the pipes also increase the resistance of the pumps and require more energy for the same flow rate. At the same time, the resulting slime layer releases gases that are hazardous to health, such as hydrogen sulphide. Pigging technology prevents this and maintains the efficiency of the pipes.
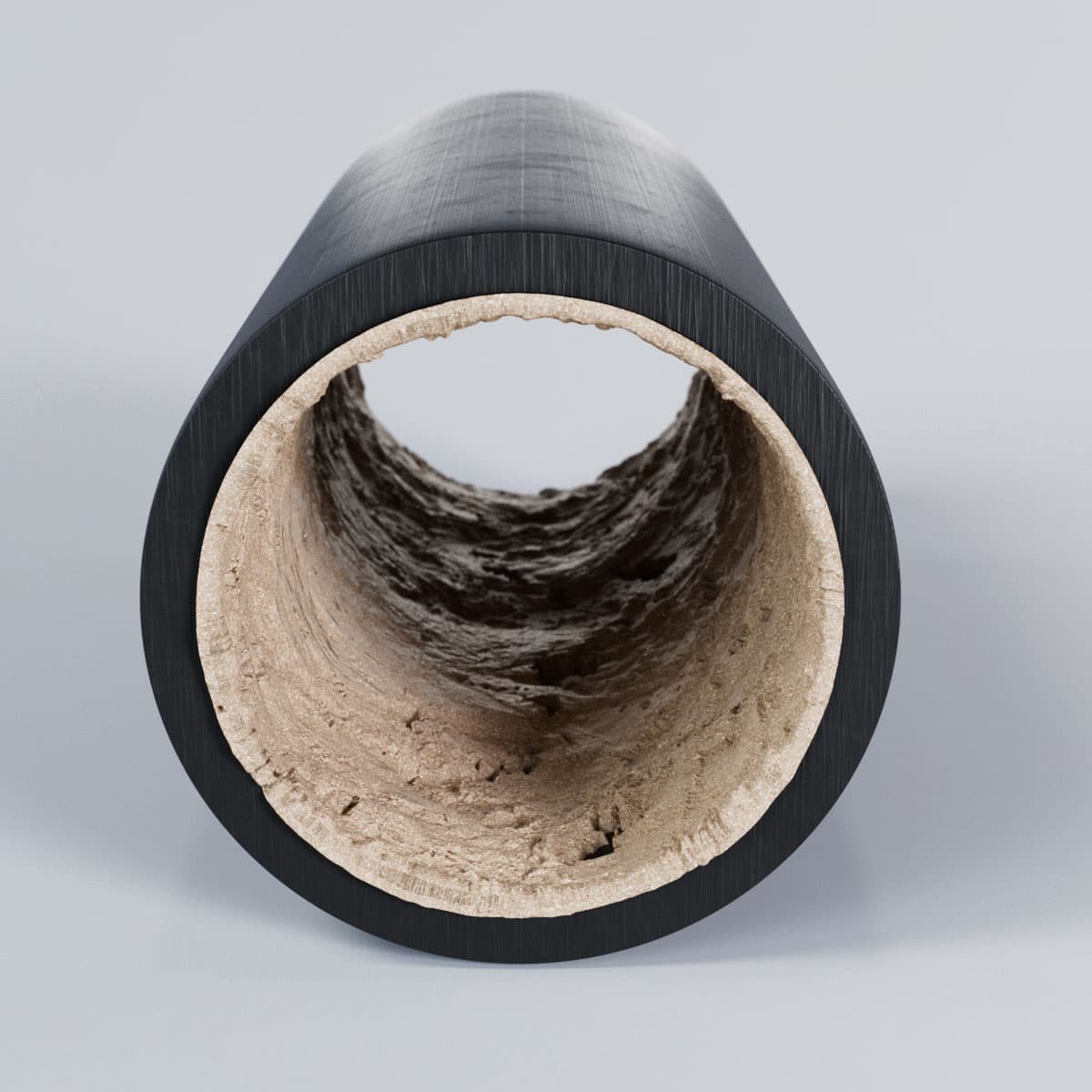


Pigging for careful inspection of the pipeline
Pigging allows leaks in pipelines to be detected and repaired in good time before major damage occurs. To ensure that the pipes remain in perfect condition, pigging should be carried out regularly. There are various types of pigs that can be used for this purpose:
MTA Measurement Technology: Pipe cleaning
Pigging procedure
During pigging, the pipe pig travels through the pipe and efficiently removes air bubbles and contaminants by pushing them out of the pipe.
Application – The function of the pig trap
Whether for cleaning or inspection purposes, the same question arises with every job: how do you insert the pig into the closed, pressurised pipeline and how do you remove it again?
To perform pigging, ideally a pig trap, also known as a pig gate, is used, which acts as a ‘transmitter’. There are two ways to pig the pipeline:
For water pipes, the pressure on the pipe is first released and the shut-off valve opened. This allows the pig to be inserted into the pigging station, for example our Quick-Pig, and the trap to be closed again. Finally, pressure is applied to the pipe and pigging can begin.


In fact, the pig can also be used in other areas during the process. It travels through the pipe with the product flow and cleans the pipe.
Pigging — The pig in the pipeline
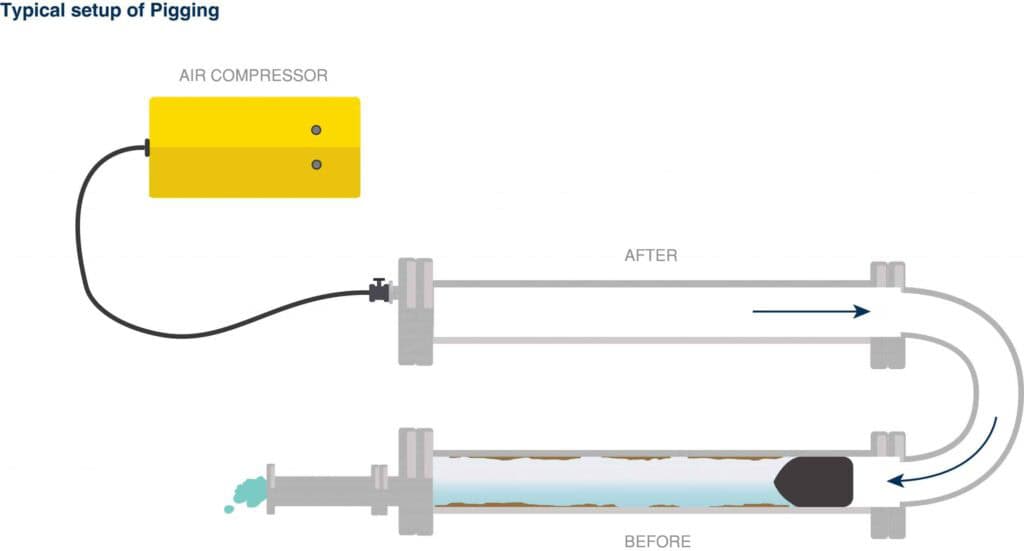
Once the pig is in the pipe, it moves forward using water and/or gas pressure. The highly accelerated leak water ensures effective cleaning and flushes contaminants out in front of the pig. At the end of the process, these can be collected and disposed of at the ‘catcher’ pig station.
Withdrawal — The open system
In an open system, also known as the one-way principle, the removal of the pig is differentiated according to the circumstances:
Pig trap:
As with pig insertion, a pig lock is used, which in this case acts as the ‘catcher’. First, the pressure is removed from the pipe and the valve is opened. The pig can then be removed using the pig station, in this case our Quick-Pig, the valve can be closed and pressure can be restored to the pipe.
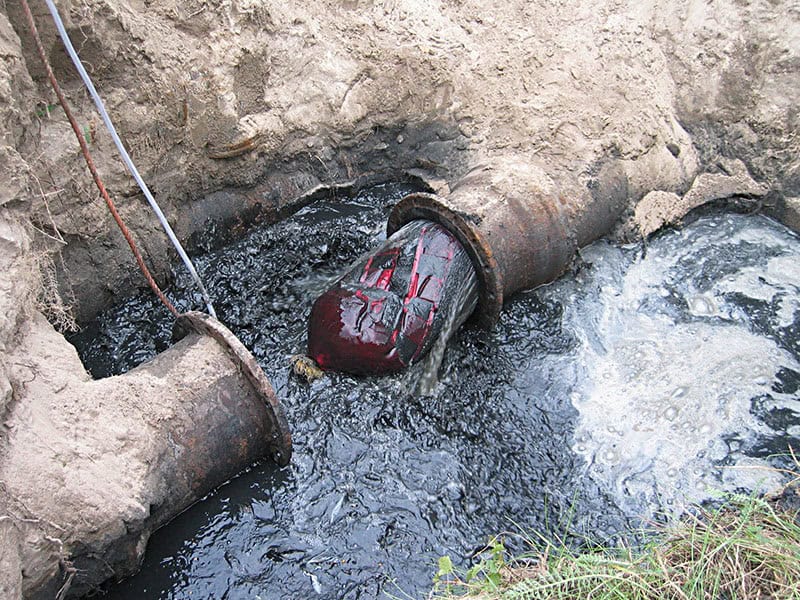


Gravity Main:
Some pipes lead directly to Gravity Mains, which means that a pig trap is not necessary. The pig is flushed out with the contents of the pipe and can then be removed.
Our pigging station has a lot to offer. See for yourself!
Areas of application for pigging technology
A wide range of industries use pigging systems, from the oil and gas industry to wastewater disposal. Pigging systems are also used in the food industry.
Pigging gas pipelines
Gas pipes are dried with air before commissioning and a pig is run through them to remove unwanted water from the pipe.
Pigging raising main systems
Waste materials and fatty acids cause incrustations in sewage pipes. This results in an unpleasant and unhealthy odour. However, this problem can be avoided thanks to pigging technology, as regular pigging keeps the pipes clean.
Pigging for drinking water pipes
Contaminants in pipes impair the quality of drinking water. A cleaning pig removes deposits, incrustations and corrosion, restoring water quality. Even in pipes that are difficult to vent, pigs can counteract hydraulic cross-sectional narrowing caused by air pockets.
The pigs can also be used for pressure testing pipelines. The company Esders from Haselünne explains on its website why this is the most effective solution: Pigging drinking water pipes
Pigging food pipes
The use of pig taps makes work in the food industry easier. Pipelines no longer need to be cleaned manually; this is done by the cleaning pig. This saves costs and energy while ensuring product safety.
Pigging pipes in the chemical industry
In the chemical industry, pipelines are often used for multiple product processes. Accordingly, the use of pigging systems should be employed to prevent the mixing of products.

Pigable pipelines: FAQ
Before a pigging system can be installed and the pig can be used, there are a few requirements to consider.
Which pipelines are piggable?
- Rising Mains
- Drinking water and raw water pipes
- Surface water pipes
- Pipes for industrial wastewater
- Pipes in the food industry
- Pipes for process water
- Pipes in the oil and gas industry
What material must the pipes be made of?
- PE 100
- PVC
- Steel
- Stainless steel
- Cast iron
What requirements must the pipes meet?
- Fittings that can fully open the pipe cross-section, such as gate valves, must be used (no flaps!).
- The internal diameter must be uniform within certain tolerances, otherwise the pig may float in the pipe and thus lose its function.
- There must be no differences in size, otherwise the pig will have to be replaced in the middle of operation, meaning that an intermediate station must be provided for the calibre change.
- The pipe must be able to withstand slight overpressure.
- The pig must be easy to insert and remove – that’s why the Quick-Pig Station was designed!
Are pigging systems only available for new pipelines?
The clear answer is no!Existing pressure pipelines with an internal pressure of up to 16 bar can be retrofitted quickly and permanently with minimal invasiveness using a compact pig trap, such as our Quick-Pig pigging station. It does not matter whether the pipeline is made of PE, PVC, steel or cast iron.
In new buildings, shafts or mole stations are already planned during the design phase.
What are the dangers of pipe cleaning?
Many fear that curves and T‑pieces in the pipes pose a danger to pipe pigs, as they could get stuck or move in the wrong direction. However, such fears are unfounded. Even 90° bends are no obstacle thanks to the flexible body of the pig.
Pigs: records from around the world
Pigging systems are used worldwide for pipelines. We have compiled a brief overview below to list records and events that we are aware of!
Do you have any additions to our list? Then please write to us!
UNIROR and the giant pig
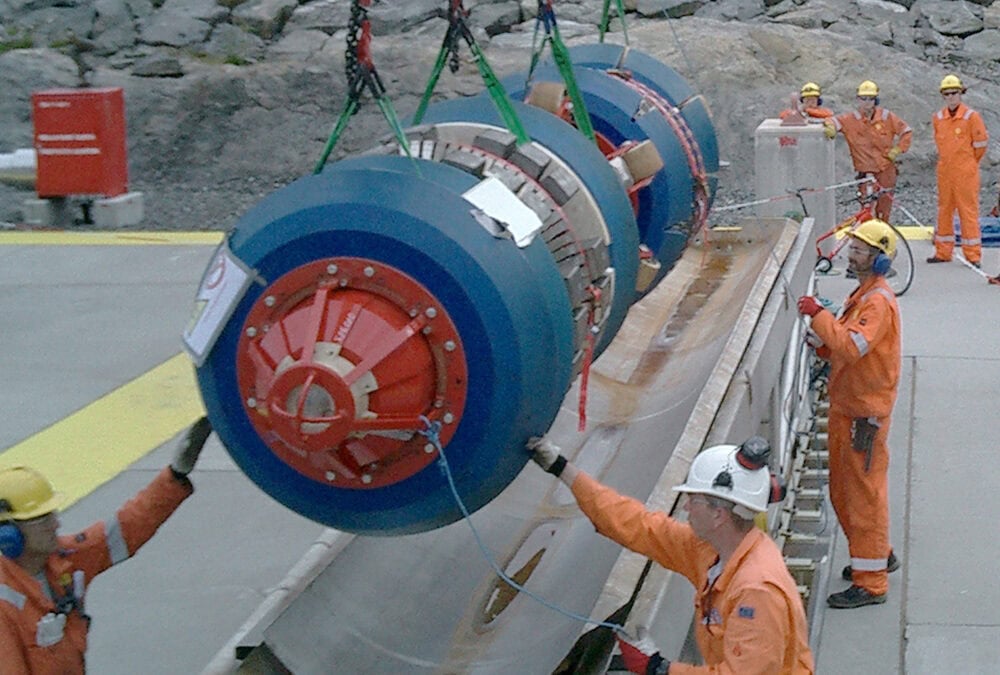
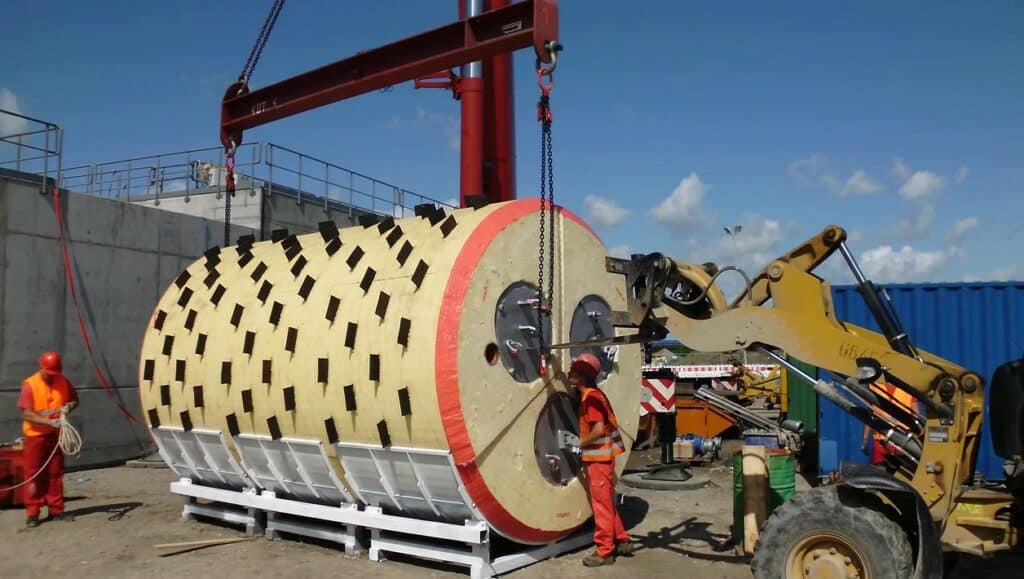
‘Nothing is impossible!’ That is the motto of Uniror, a company based in Forst, Germany. They have designed an impressive giant pig for a contaminated cooling water pipe. The pig has a diameter of over 3000 mm for the nominal width DN 3400 and weighs 30 tonnes. This makes it the largest known cleaning pig in the world. Further information is available here: UNIROR

Nord Stream 2 pipeline to be inspected
With an astonishing length of 1,224 km, the Nord Stream pipeline is the longest pipeline ever pigged. Rosen GmbH, based in Lingen, developed the pipe pigs used in Russia, which, according to the company, will arrive in Germany in 10 days.
London’s fatberg
This event may not be directly related to pipe molching, but it is so fascinating and cautionary at the same time that we had to include it in our list.
Huge deposits and waste materials, known as ‘fatbergs’, have been found several times in London’s sewer system. In autumn 2017, the largest known fatberg was discovered, measuring an impressive 250 metres in length and weighing 130 tonnes. It took nine weeks to remove it, and a remaining piece was later even exhibited in a museum.

James Bond 007 – Experiences with the Pipeline
Whether in 1987, when James Bond helped a Soviet general escape to another country through a pipeline using a mole in ‘The Living Daylights’, or in 1999, when Bond himself travelled through pipes using a mole in ‘The World Is Not Enough’ – moles also play an important role in films!
James Bond 007 — The Living Daylights
James Bond 007 — The World Is Not Enough







